Orthodontic Treatment Age
Orthodontic Treatment Age
A
child’s first orthodontic examination by an orthodontist should ideally be
performed around the age of six.
Developmental
and functional disorders are significantly easier to treat when early
intervention is provided. For example, in children with habits such as thumb
sucking, mouth breathing, or tongue-thrust swallowing, early identification and
elimination of these habits is critically important. When such unfavorable
habits lead to jaw discrepancies, early orthodontic intervention becomes
essential.
If,
during childhood, the only problem present is dental crowding and the facial
appearance and jaw structure are otherwise normal, the most appropriate time
for orthodontic treatment is generally when all or nearly all primary teeth
have been exfoliated and the permanent teeth have erupted. This typically
corresponds to approximately 10–11 years of age in girls and 11–12 years of age
in boys.
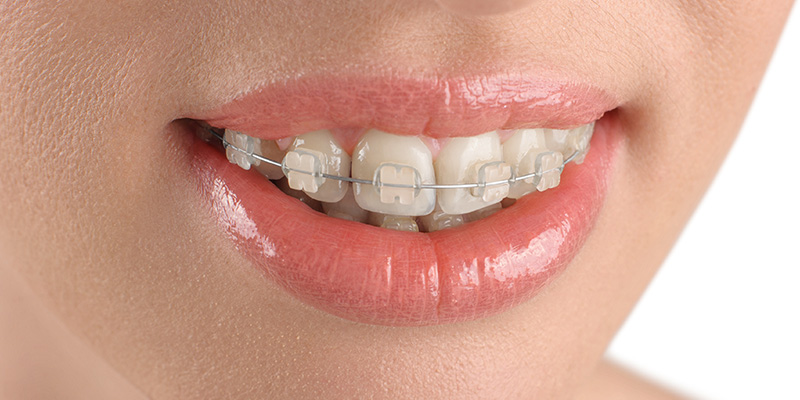
TYPES OF BRACKETS
If the orthodontist and the patient decide
on fixed orthodontic treatment, either metal or ceramic (esthetic) brackets may
be selected. Although metal brackets are commonly preferred, ceramic brackets
are often chosen for patients with higher esthetic expectations.
In both treatment modalities, meticulous
tooth brushing is essential to prevent dental caries. At the end of treatment
with ceramic brackets, discoloration or staining of the brackets may occur.
Additionally, due to increased fiction between the archwire and the bracket in
ceramic systems, treatment duration may be prolonged. Your orthodontist will
recommend the most appropriate treatment option based on your individual needs.
As an alternative to esthetic brackets, clear aligner treatment systems have
become increasingly popular in recent years.
The archwire used in bracket systems
function by applying controlled forces to move the teeth in the desired
direction. Treatment duration generally ranges from 1 to 3 years. Since teeth
gradually change position throughout treatment, monthly follow-up appointments
are required.
In the past, brackets consisted of thick
steel bands encircling the teeth. With advancements in technology, brackets
have become significantly smaller, and orthodontic bands are now rarely used.
During placement, the orthodontist bonds small brackets to the teeth using special
adhesives, after which archwires are inserted through the brackets. These
archwires guide the movement of the teeth along a predetermined path. Small
elastic ligatures, either transparent or colored according to patient
preference, may be used to secure the archwires to the brackets.
ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT METHODS
There
are essentially two main types of orthodontic treatment methods: removable
appliances, which the patient can insert and remove independently, and fixed
appliances, which are bonded to the teeth by the orthodontist. Each of these
categories includes several subtypes.
For
example, removable appliances may be used for active treatment or for retention
following treatment. Fixed appliances may include wires bonded to the lingual
(inner) surfaces of the teeth (lingual retainers) or metal and esthetic
brackets bonded to the labial (outer) surfaces.
Each
patient’s orthodontic problem and expectations are unique; therefore, the most
suitable treatment approach must be determined individually. Materials and
treatment modalities may vary among patients. Just as the appropriate age for
treatment differs from person to person, treatment duration also depends on the
nature and severity of the orthodontic problem.
The
shortest treatment duration is approximately six months. Most treatments last
between one and two years, while some may extend to two or three years. In
certain special conditions, such as cleft lip and palate, treatment duration
may be longer.
Orthodontic
treatment is not a painful procedure. During the first one to two weeks, minor
discomfort related to the adaptation process may be experienced. Apart from
this initial period, patients can continue their normal daily lives while
paying some attention to dietary habits. Monthly visits to the orthodontist are
necessary for monitoring, adjustments, and appliance modifications.
